Integrating the Chess Library: Move History and Game State Management
Building a Chess TUI with Go and Bubble Tea - Part 2
In Part 1, we built a solid TUI foundation with cursor navigation and board rendering. Now it’s time to make it play actual chess.
This iteration proved more complex than anticipated. Rather than implementing chess rules from scratch, I discovered that properly integrating an existing chess library is the smarter approach. A comprehensive tutorial by Andy Williams on integrating chess libraries into Fyne applications provided crucial insights into working with github.com/corentings/chess/v2.
What This Post Covers
The key changes in this iteration:
- Delegating to the chess library: Moving away from custom piece management to leverage battle-tested chess logic
- Coordinate mapping: Implementing
coordinatesToSquareto translate terminal coordinates (x, y) into the library’s square indices - Move history tracking: Building a move list that displays game progression
- Game outcome detection: Recognizing checkmate, stalemate, and other end conditions
By the end of this post, you’ll have a fully functional chess game that validates moves, tracks history, and detects game outcomes.
Previous Post
If you haven’t read the first post about building the foundation of this chess TUI, check it out here: Go Chess TUI with Bubble Tea Foundation
The Big Refactor: Delegating to the Chess Library
The most significant change in this iteration was moving away from custom piece management to fully leveraging the github.com/corentings/chess/v2 library. Instead of maintaining our own board [8][8]Piece array and implementing chess rules from scratch, we now let the library handle:
- Board state management
- Move validation
- Legal move generation
- Game outcome detection (checkmate, stalemate, draws)
- All chess rules including castling, en passant, and pawn promotion
Code Cleanup
Here’s what was removed:
// Removed custom types
type PieceType int
const (
Empty PieceType = iota
Pawn
Knight
// ... etc
)
type Color int
type Piece struct {
Type PieceType
Color Color
}
// Removed custom board state
type model struct {
// ...
board [8][8]Piece // No longer needed!
}And replaced with the library’s built-in types:
// Using the chess library
type model struct {
cursorX int
cursorY int
selected bool
selectedX int
selectedY int
status string
showCoords bool
showHistory bool
game *chess.Game // Single source of truth
}Understanding coordinatesToSquare
The chess library uses a linear indexing system for squares (0-63), while our TUI uses a 2D coordinate system (x, y). The coordinatesToSquare function bridges these two representations:
// coordinatesToSquare converts x,y board coordinates to chess library square index (0-63)
// x: 0-7 (files a-h), y: 0-7 (ranks 8-1)
func coordinatesToSquare(x, y int) chess.Square {
rank := 7 - y // y=0 is rank 8, y=7 is rank 1
file := x
return chess.Square(rank*8 + file)
}How it works:
-
Rank Conversion: Our TUI displays the board with y=0 at the top (rank 8) and y=7 at the bottom (rank 1). The chess library expects rank 0 at the bottom, so we flip it:
rank = 7 - y -
Linear Index Calculation: A chessboard has 8 files (a-h) and 8 ranks (1-8). To convert from 2D to 1D:
- Each rank contains 8 squares
- Square index =
rank * 8 + file
Examples:
- Square a1 (bottom-left): x=0, y=7 → rank=0, file=0 → index = 0*8 + 0 = 0
- Square h1 (bottom-right): x=7, y=7 → rank=0, file=7 → index = 0*8 + 7 = 7
- Square a8 (top-left): x=0, y=0 → rank=7, file=0 → index = 7*8 + 0 = 56
- Square h8 (top-right): x=7, y=0 → rank=7, file=7 → index = 7*8 + 7 = 63
- Square e4 (center): x=4, y=4 → rank=3, file=4 → index = 3*8 + 4 = 28
This mapping is crucial because every interaction with the chess library requires square indices, not x/y coordinates.
Rendering Pieces from the Library
Instead of maintaining our own piece positions, we now query the library’s board state:
// Get piece from chess library's board
square := coordinatesToSquare(x, y)
piece := m.game.Position().Board().Piece(square)
cellContent := chessPieceSymbol(piece)The chessPieceSymbol function maps the library’s piece types to Unicode chess symbols:
func chessPieceSymbol(p chess.Piece) string {
symbols := map[chess.PieceType]map[chess.Color]string{
chess.Pawn: {chess.White: " ♙ ", chess.Black: " ♟ "},
chess.Knight: {chess.White: " ♘ ", chess.Black: " ♞ "},
chess.Bishop: {chess.White: " ♗ ", chess.Black: " ♝ "},
chess.Rook: {chess.White: " ♖ ", chess.Black: " ♜ "},
chess.Queen: {chess.White: " ♕ ", chess.Black: " ♛ "},
chess.King: {chess.White: " ♔ ", chess.Black: " ♚ "},
chess.NoPieceType: {chess.NoColor: " · "},
}
if colorMap, ok := symbols[p.Type()]; ok {
if symbol, ok := colorMap[p.Color()]; ok {
return symbol
}
}
return " · "
}Move Validation and Execution
Move validation is now dramatically simpler. Instead of implementing chess rules ourselves, we just check if the move is in the library’s list of valid moves:
func (m *model) isValidMove(fromX, fromY, toX, toY int) bool {
// Build move string in UCI format (e.g., "e2e4")
fromSquare := squareName(fromX, fromY)
toSquare := squareName(toX, toY)
moveStr := fromSquare + toSquare
// Check if this move is in the list of valid moves
for _, move := range m.game.ValidMoves() {
if move.String() == moveStr {
return true
}
}
return false
}Move execution is equally straightforward:
// Find and execute the move
var moveToExecute *chess.Move
for _, move := range m.game.ValidMoves() {
if move.String() == moveStr {
moveToExecute = &move
break
}
}
if moveToExecute != nil {
if err := m.game.Move(moveToExecute, nil); err != nil {
// Handle error
}
// Move executed successfully!
}Enhanced Status Messages
The status bar now shows descriptive information about each move:
// Format descriptive move message
colorName := "White"
if movingPiece.Color() == chess.Black {
colorName = "Black"
}
pieceNames := map[chess.PieceType]string{
chess.Pawn: "pawn",
chess.Knight: "knight",
chess.Bishop: "bishop",
chess.Rook: "rook",
chess.Queen: "queen",
chess.King: "king",
}
pieceName := pieceNames[movingPiece.Type()]
m.status = fmt.Sprintf("%s %s to %s", colorName, pieceName, to)Now instead of seeing “Moved: e2 -> e4”, you see “White pawn to e4”.
Move History Display
Pressing the ‘h’ key toggles a move history display that shows all moves played so far:
if m.showHistory {
moves := m.game.Moves()
if len(moves) > 0 {
out.WriteString("\nMove History:\n")
// Display moves in pairs (White, Black)
for i := 0; i < len(moves); i += 2 {
moveNum := (i / 2) + 1
whiteMoveStr := moves[i].String()
if i+1 < len(moves) {
blackMoveStr := moves[i+1].String()
fmt.Fprintf(&out, "%d. %s %s\n", moveNum, whiteMoveStr, blackMoveStr)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(&out, "%d. %s\n", moveNum, whiteMoveStr)
}
}
}
}Example output:
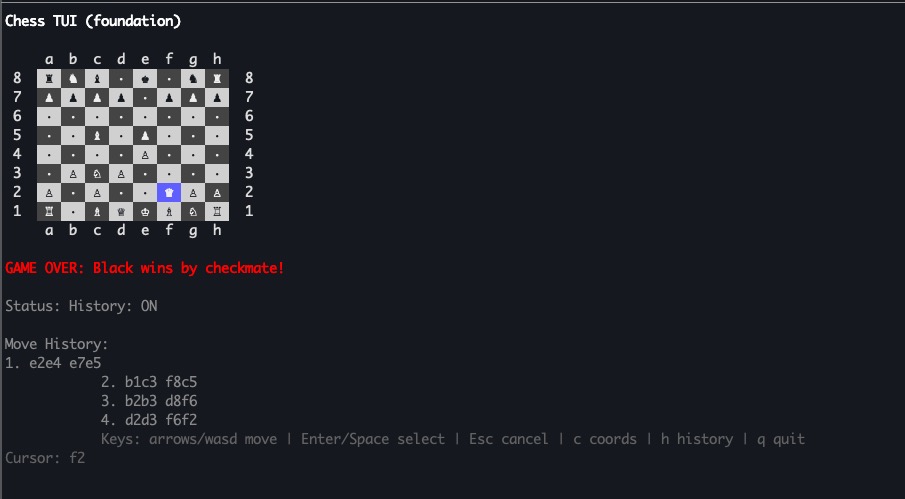
Move History:
1. e2e4 e7e5
2. g1f3 b8c6
3. f1c4 g8f6Game Outcome Detection
The library automatically tracks game state, allowing us to detect when the game ends:
outcome := m.game.Outcome()
if outcome != chess.NoOutcome {
switch outcome {
case chess.WhiteWon:
out.WriteString("GAME OVER: White wins by checkmate!\n")
case chess.BlackWon:
out.WriteString("GAME OVER: Black wins by checkmate!\n")
case chess.Draw:
method := m.game.Method()
switch method {
case chess.Stalemate:
out.WriteString("GAME OVER: Draw by stalemate\n")
case chess.ThreefoldRepetition:
out.WriteString("GAME OVER: Draw by threefold repetition\n")
case chess.FiftyMoveRule:
out.WriteString("GAME OVER: Draw by fifty-move rule\n")
case chess.InsufficientMaterial:
out.WriteString("GAME OVER: Draw by insufficient material\n")
}
}
}The library handles all the complex logic for detecting:
- Checkmate
- Stalemate
- Threefold repetition
- Fivefold repetition
- Fifty-move rule
- Seventy-five-move rule
- Insufficient material
Updated Controls
The TUI now supports:
- Arrow keys / WASD: Move cursor
- Enter / Space: Select piece or destination
- Esc: Cancel selection
- c: Toggle coordinate display
- h: Toggle move history (new!)
- q: Quit
What’s Next?
Now that we have a fully functional chess game with proper rules enforcement and game state management, the next steps could include:
- Stockfish Integration: Add AI opponent using the Stockfish engine via UCI protocol
- Time Controls: Implement chess clocks for timed games
- PGN Export: Save games in standard Portable Game Notation format
- Move Highlights: Show legal moves for the selected piece
- Captured Pieces Display: Show which pieces have been captured
- Opening Book: Display opening names from a database
Conclusion
By delegating to the chess library instead of implementing rules from scratch, we’ve:
- Reduced code complexity significantly
- Eliminated potential bugs in chess rule implementation
- Gained access to advanced features like draw detection
- Made the codebase more maintainable
The most complex part of the integration was understanding the coordinate system mapping, but once that was sorted out with the coordinatesToSquare function, everything else fell into place naturally.
Here is the full source code for now, everything lives in a single file for simplicity:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"strings"
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
"github.com/corentings/chess/v2"
)
const boardSize = 8
type model struct {
cursorX int
cursorY int
selected bool
selectedX int
selectedY int
status string
showCoords bool
showHistory bool
game *chess.Game
}
func initialModel() model {
game := chess.NewGame()
m := model{
cursorX: 4,
cursorY: 4,
selected: false,
status: "Arrow keys move. Enter selects. Esc cancels. c toggles coords. h toggles history. q quits.",
showCoords: true,
showHistory: false,
game: game,
}
return m
}
func (m model) Init() tea.Cmd { return nil }
func clamp(v, lo, hi int) int {
if v < lo {
return lo
}
if v > hi {
return hi
}
return v
}
func squareName(x, y int) string {
file := byte('a' + x)
rank := byte('8' - y)
return string([]byte{file, rank})
}
// coordinatesToSquare converts x,y board coordinates to chess library square index (0-63)
// x: 0-7 (files a-h), y: 0-7 (ranks 8-1)
func coordinatesToSquare(x, y int) chess.Square {
rank := 7 - y // y=0 is rank 8, y=7 is rank 1
file := x
return chess.Square(rank*8 + file)
}
// chessPieceSymbol converts chess library's piece to display symbol
func chessPieceSymbol(p chess.Piece) string {
symbols := map[chess.PieceType]map[chess.Color]string{
chess.Pawn: {chess.White: " ♙ ", chess.Black: " ♟ "},
chess.Knight: {chess.White: " ♘ ", chess.Black: " ♞ "},
chess.Bishop: {chess.White: " ♗ ", chess.Black: " ♝ "},
chess.Rook: {chess.White: " ♖ ", chess.Black: " ♜ "},
chess.Queen: {chess.White: " ♕ ", chess.Black: " ♛ "},
chess.King: {chess.White: " ♔ ", chess.Black: " ♚ "},
chess.NoPieceType: {chess.NoColor: " · "},
}
if colorMap, ok := symbols[p.Type()]; ok {
if symbol, ok := colorMap[p.Color()]; ok {
return symbol
}
}
return " · "
}
func (m model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (tea.Model, tea.Cmd) {
switch msg := msg.(type) {
case tea.KeyMsg:
switch msg.String() {
case "q", "ctrl+c":
return m, tea.Quit
case "c":
m.showCoords = !m.showCoords
if m.showCoords {
m.status = "Coordinates: ON"
} else {
m.status = "Coordinates: OFF"
}
return m, nil
case "h":
m.showHistory = !m.showHistory
if m.showHistory {
m.status = "History: ON"
} else {
m.status = "History: OFF"
}
return m, nil
case "esc":
m.selected = false
m.status = "Selection cleared."
return m, nil
case "up", "w":
m.cursorY = clamp(m.cursorY-1, 0, boardSize-1)
case "down", "s":
m.cursorY = clamp(m.cursorY+1, 0, boardSize-1)
case "left", "a":
m.cursorX = clamp(m.cursorX-1, 0, boardSize-1)
case "right", "d":
m.cursorX = clamp(m.cursorX+1, 0, boardSize-1)
case "enter", " ":
if !m.selected {
m.selected = true
m.selectedX, m.selectedY = m.cursorX, m.cursorY
// Get piece from chess library board
square := coordinatesToSquare(m.selectedX, m.selectedY)
piece := m.game.Position().Board().Piece(square)
if piece.Type() == chess.NoPieceType {
m.status = "No piece at " + squareName(m.selectedX, m.selectedY)
m.selected = false
return m, nil
}
colorName := "white"
if piece.Color() == chess.Black {
colorName = "black"
}
m.status = fmt.Sprintf("Selected %s piece at %s. Pick destination and press Enter.",
colorName,
squareName(m.selectedX, m.selectedY),
)
return m, nil
}
// Try to execute the move
from := squareName(m.selectedX, m.selectedY)
to := squareName(m.cursorX, m.cursorY)
moveStr := from + to
// Get the piece before moving
fromSquare := coordinatesToSquare(m.selectedX, m.selectedY)
movingPiece := m.game.Position().Board().Piece(fromSquare)
// Find and execute the move
var moveToExecute *chess.Move
for _, move := range m.game.ValidMoves() {
if move.String() == moveStr {
moveToExecute = &move
break
}
}
if moveToExecute != nil {
// Execute the move through chess library
if err := m.game.Move(moveToExecute, nil); err != nil {
m.selected = false
m.status = fmt.Sprintf("Error executing move: %v", err)
return m, nil
}
// Format descriptive move message
colorName := "White"
if movingPiece.Color() == chess.Black {
colorName = "Black"
}
pieceNames := map[chess.PieceType]string{
chess.Pawn: "pawn",
chess.Knight: "knight",
chess.Bishop: "bishop",
chess.Rook: "rook",
chess.Queen: "queen",
chess.King: "king",
}
pieceName := pieceNames[movingPiece.Type()]
m.selected = false
m.status = fmt.Sprintf("%s %s to %s", colorName, pieceName, to)
} else {
m.selected = false
m.status = fmt.Sprintf("Invalid move: %s -> %s", from, to)
}
return m, nil
}
}
return m, nil
}
func (m model) View() string {
titleStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Bold(true)
statusStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("245"))
helpStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("241"))
light := lipgloss.NewStyle().Background(lipgloss.Color("252")).Foreground(lipgloss.Color("0"))
dark := lipgloss.NewStyle().Background(lipgloss.Color("238")).Foreground(lipgloss.Color("255"))
cursorStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().
Background(lipgloss.Color("63")).
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("255")).
Bold(true)
selectedStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().
Background(lipgloss.Color("135")).
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("0")).
Bold(true)
var out strings.Builder
out.WriteString(titleStyle.Render("Chess TUI (foundation)") + "\n\n")
if m.showCoords {
out.WriteString(" ")
for x := range boardSize {
fmt.Fprintf(&out, " %c ", 'a'+x)
}
out.WriteString("\n")
}
for y := range boardSize {
if m.showCoords {
fmt.Fprintf(&out, " %d ", 8-y)
}
for x := range boardSize {
isLight := (x+y)%2 == 0
style := dark
if isLight {
style = light
}
if m.selected && x == m.selectedX && y == m.selectedY {
style = selectedStyle
}
if x == m.cursorX && y == m.cursorY {
style = cursorStyle
}
// Get piece from chess library's board
square := coordinatesToSquare(x, y)
piece := m.game.Position().Board().Piece(square)
cellContent := chessPieceSymbol(piece)
out.WriteString(style.Render(cellContent))
}
if m.showCoords {
fmt.Fprintf(&out, " %d", 8-y)
}
out.WriteString("\n")
}
if m.showCoords {
out.WriteString(" ")
for x := range boardSize {
fmt.Fprintf(&out, " %c ", 'a'+x)
}
out.WriteString("\n")
}
// Check if game is over
outcome := m.game.Outcome()
if outcome != chess.NoOutcome {
gameOverStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Bold(true).Foreground(lipgloss.Color("196"))
switch outcome {
case chess.WhiteWon:
out.WriteString("\n" + gameOverStyle.Render("GAME OVER: White wins by checkmate!") + "\n")
case chess.BlackWon:
out.WriteString("\n" + gameOverStyle.Render("GAME OVER: Black wins by checkmate!") + "\n")
case chess.Draw:
method := m.game.Method()
drawReason := "draw"
switch method {
case chess.Stalemate:
drawReason = "stalemate"
case chess.ThreefoldRepetition:
drawReason = "threefold repetition"
case chess.FivefoldRepetition:
drawReason = "fivefold repetition"
case chess.FiftyMoveRule:
drawReason = "fifty-move rule"
case chess.SeventyFiveMoveRule:
drawReason = "seventy-five-move rule"
case chess.InsufficientMaterial:
drawReason = "insufficient material"
}
out.WriteString("\n" + gameOverStyle.Render(fmt.Sprintf("GAME OVER: Draw by %s", drawReason)) + "\n")
}
}
out.WriteString("\n" + statusStyle.Render("Status: "+m.status) + "\n")
// Show move history if enabled
if m.showHistory {
moves := m.game.Moves()
if len(moves) > 0 {
historyStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("245"))
out.WriteString("\n" + historyStyle.Render("Move History:") + "\n")
// Display moves in pairs (White, Black)
for i := 0; i < len(moves); i += 2 {
moveNum := (i / 2) + 1
whiteMoveStr := moves[i].String()
if i+1 < len(moves) {
blackMoveStr := moves[i+1].String()
out.WriteString(historyStyle.Render(fmt.Sprintf("%d. %s %s\n", moveNum, whiteMoveStr, blackMoveStr)))
} else {
out.WriteString(historyStyle.Render(fmt.Sprintf("%d. %s\n", moveNum, whiteMoveStr)))
}
}
}
}
out.WriteString(helpStyle.Render("Keys: arrows/wasd move | Enter/Space select | Esc cancel | c coords | h history | q quit") + "\n")
out.WriteString(helpStyle.Render(
fmt.Sprintf("Cursor: %s", squareName(m.cursorX, m.cursorY)),
) + "\n")
return out.String()
}
func main() {
p := tea.NewProgram(initialModel(), tea.WithAltScreen())
if _, err := p.Run(); err != nil {
fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}Links
- Previous post: Go Chess TUI with Bubble Tea Foundation
- Tutorial video: Building Chess in Go with Fyne
- Chess library: github.com/corentings/chess/v2
- Bubble Tea framework: github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea